

The dose of acetylcysteine should be calculated based upon body weight and estimated time and acetaminophen ingestion. Acetylcysteine is available as effervescent tablets of 5 mg (Cetylev) for oral use and as a solution for injection in single dose vials of 200 mg/mL (Acetadote).
An oral form of acetylcysteine was approved for use as an acetaminophen antidote in 1978, and an intravenous formulation in 2004. Acetylcysteine also has mucolytic activity and was initially approved for use in humans in 1963 as Mucomyst, a solution for inhalation that helps to emulsify respiratory secretions in patients with pulmonary infections or chronic bronchitis. Subsequent studies suggested that administration even after 10 hours was partially effective and may also be beneficial in other, non-acetaminophen causes of acute liver failure, including drug induced liver injury. In multiple clinical trials, administration of acetylcysteine (also referred to as N-acetylcysteine or NAC) within 10 hours of an acetaminophen overdose effectively prevented serious liver injury. Restoration of glutathione stores ameliorates the cell injury from acetaminophen. Glutathione can become depleted in patients with malnutrition, chronic debilitating illnesses and chronic alcoholism, and becomes acutely depleted in patients with acetaminophen overdose leading to formation of toxic adducts of acetaminophen metabolites with essential intracellular molecules. Cysteine itself has a disagreeable odor and taste, while acetylated cysteine is more palatable and maintains the ability to support glutathione synthesis. Importantly, cysteine is required for synthesis of glutathione (a tripeptide of cysteine, glycine and glutamic acid) that is an essential intracellular antioxidant, providing protection against free radicals and other intracellular toxins including intermediates of drug metabolism.
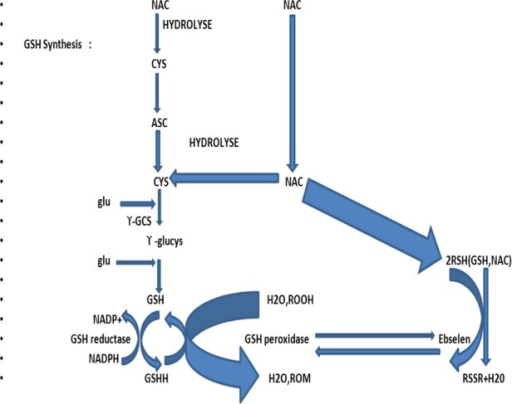
The amino acid cysteine has a thiol side chain that can undergo redox reactions and thus has antioxidant activity. Acetylcysteine (a seet" il sis' teen) is a modified amino acid that is used to reverse the toxic effects of acetaminophen overdose and prevent acute liver failure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
